An infection with the new Mpox variant clade 1b has been detected in Germany for the first time, the Robert Koch Institute health authority said on Tuesday 22 October.
Germany: the latest site of an Mpox infection
The Mpox infection occurred abroad and was detected last Friday, the institute said, adding that it did not see an increased risk for Germany but was “monitoring the situation very closely”.
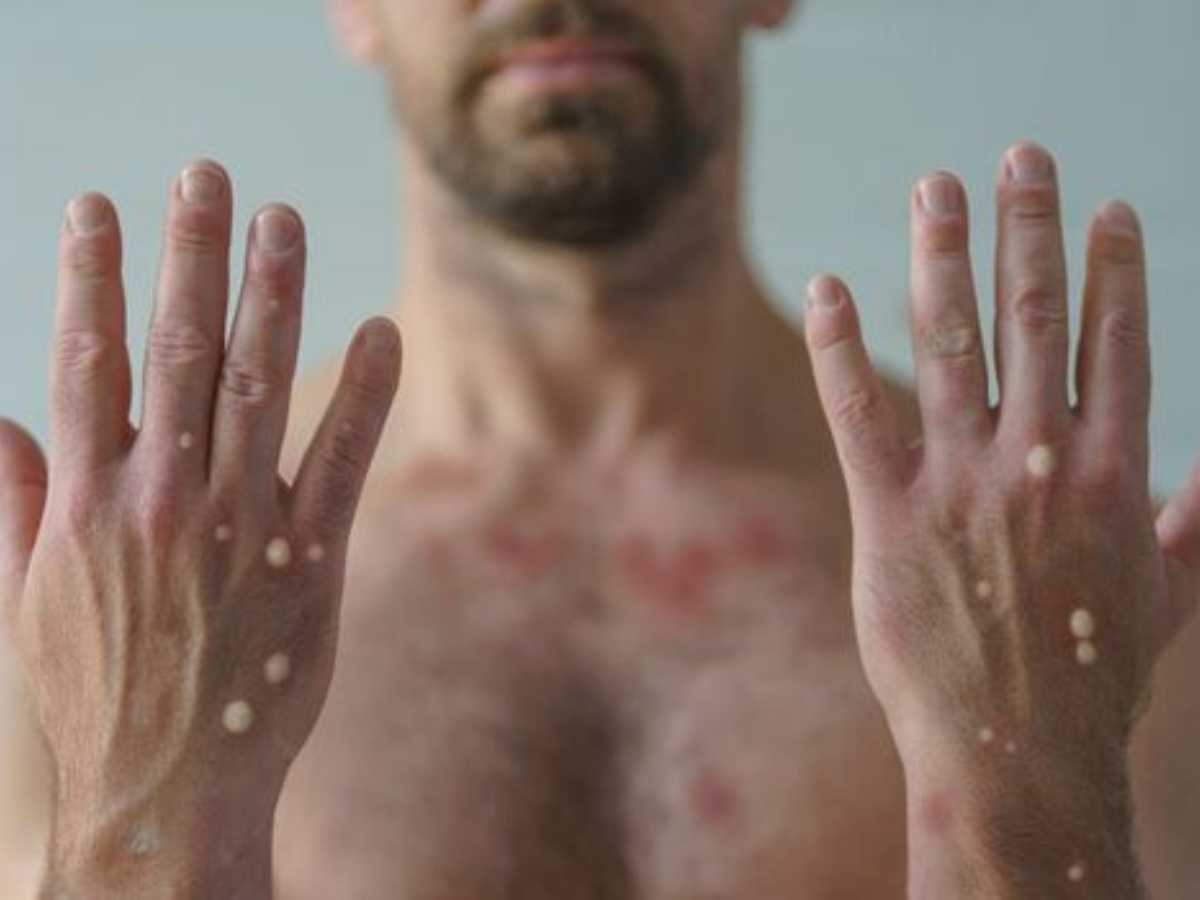
Mpox, a viral disease related to smallpox that causes fever, body aches, swollen lymph nodes and a rash that forms into blisters, has two main subtypes – clade 1 and clade 2.
From May 2022, clade 2 spread around the world, mostly affecting gay and bisexual men in Europe and the US. In July 2022, the World Health Organisation (WHO) declared an international public health emergency, its highest level of alarm over the spread.
Vaccination and awareness drives in many countries helped stem the number of worldwide cases and the WHO lifted the emergency in May 2023 after reporting 140 deaths out of roughly 87,400 cases.
But this year, a new epidemic has broken out in the Democratic Republic of Congo. As well as clade 1, which mainly affects children, a new strain emerged in the DRC, called clade 1b.
Clade 1b cases have also been recorded in nearby Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda – none of which had previously detected mpox.
In August, the WHO declared mpox (monkeypox) a global public health emergency after its surge in Africa.
WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus told a press conference:
Today, the emergency committee met and advised me that in its view, the situation constitutes a public health emergency of international concern. I have accepted that advice.
Mpox: now a global public health emergency
The gathering of 16 international figures came after the African Union’s health watchdog declared its own public health emergency over the growing outbreak.
Mpox has swept through the Democratic Republic of Congo, where the virus formerly called monkeypox was first discovered in humans in 1970, and spread to other countries.
WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said the more than 14,000 cases and 524 deaths reported so far this year in DR Congo has already exceeded last year’s total:
The emergence last year and rapid spread of clade 1b in DRC, which appears to be spreading mainly through sexual networks, and its detection in countries neighbouring DRC is especially concerning, and one of the main reasons for my decision to convene this emergency committee.
In the past month, about 90 cases of clade 1b have been reported in four countries neighbouring the DRC that have not reported mpox before: Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda.
But we are not dealing with one outbreak of one clade: we are dealing with several outbreaks of different clades in different countries with different modes of transmission and different levels of risk.
The committee advised Ghebreyesus the outbreak represents a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) — the highest alarm the WHO can sound. A PHEIC declaration then triggers emergency responses in countries worldwide under the legally binding International Health Regulations.
Deadly and dangerous
It is the second PHEIC in succession on mpox — albeit one focused on a different, and more deadly, strain of the virus. In May 2022, mpox infections surged worldwide, mostly affecting gay and bisexual men, due to the Clade 2b subclade.
The WHO declared a public health emergency which lasted from July 2022 to May 2023. The outbreak, which has now largely subsided, caused some 140 deaths out of around 90,000 cases. The clade 1b subclade, which has been surging in the DRC since September 2023, causes more severe disease than clade 2b, with a higher fatality rate.
Mpox is an infectious disease caused by a virus transmitted to humans by infected animals but can also be passed from human to human through close physical contact.
The disease causes fever, muscular aches and large boil-like skin lesions. Two vaccines for mpox are recommended by WHO immunisation experts.
A PHEIC has only been declared seven times since 2009: over H1N1 swine flu, poliovirus, Ebola, Zika virus, Ebola again, Covid-19 and mpox.
An emergency response to mpox needed
Marion Koopmans, director of the Pandemic and Disaster Management Centre at Erasmus University Rotterdam, said a PHEIC:
raises the level of alert, globally, and may allow WHO to access funds for emergency response… [but] the same priorities remain: investing in diagnostic capacity, public health response, treatment support and vaccination.
And at a global level, she said:
despite having the resources and basic public health capacity in place, the international outbreak that started in 2022 was not contained.
The Red Cross said it was scaling up preparedness measures across Africa, notably in the heavily affected eastern DRC. The International Federation of the Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies voiced “profound concern” over the spread of the virus.
The IFRC said:
This new variant is affecting a wide range of demographics, with ongoing community transmission occurring without zoonotic exposure, unlike the previous outbreaks in 2022 and 2023.
With its broad network, the IFRC said it was prepared to “play a crucial role in containing the spread of the disease, even in the hard-to-reach areas where the need is the greatest”.
Germany is monitoring the new case.
Feature image via the Canary
Additional reporting via Agence France-Presse